
As technology becomes increasingly integrated into our lives, the environmental impact of hardware production, use, and disposal becomes more critical. While technology offers countless benefits, its environmental footprint can be substantial, demanding responsible action from manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers alike.
Technology hardware plays a vital role in modern life, but its production, use, and disposal have a significant environmental impact. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas of concern:
“The question is not whether technology will save us, but whether we will save technology.”
Ursula K. Le Guin, American author

1. Resource depletion:
- Extraction of raw materials like rare earth metals, precious metals, and fossil fuels used in hardware production leads to environmental damage and resource depletion.
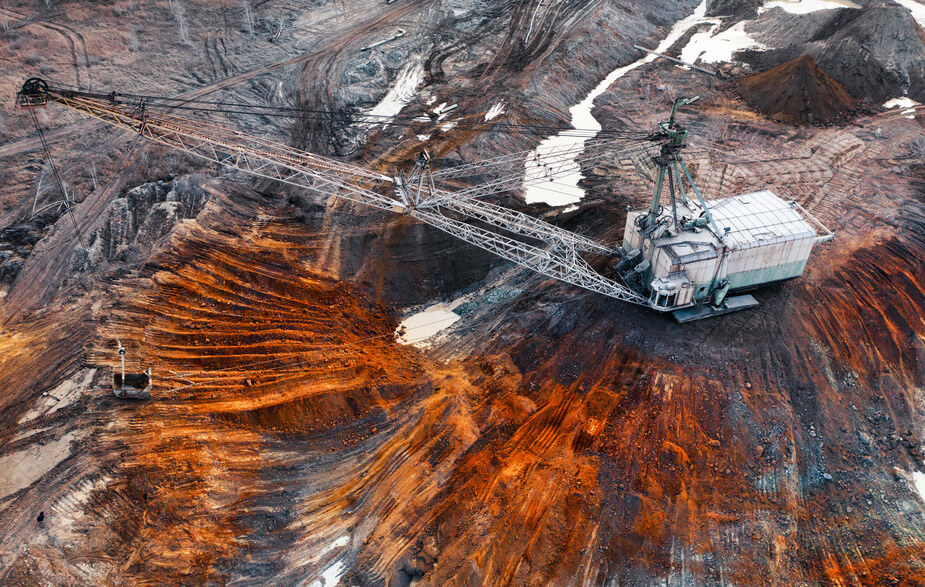

- The mining process can contribute to deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution.
2. Greenhouse gas emissions:
- Manufacturing hardware requires significant energy, often from fossil fuels, leading to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Data centers, which store and process vast amounts of data, are significant energy consumers, contributing to the carbon footprint of the tech industry.
3. E-waste:
- Rapid technological advancements lead to frequent device upgrades and disposals, generating large amounts of electronic waste (e-waste).
- E-waste often contains hazardous materials like mercury, lead, and cadmium, which can pollute the environment if not disposed of properly.
4. Water pollution:
- Semiconductor manufacturing, a crucial step in hardware production, uses large amounts of water and generates wastewater containing toxic chemicals.
- This wastewater can pollute rivers and harm aquatic life if not treated properly.
5. Human health risks:
- Workers involved in mining, manufacturing, and recycling of hardware can be exposed to hazardous chemicals and materials, leading to health risks.
- Additionally, the disposal of e-waste in landfills can release harmful toxins into the environment, impacting human health.
Solutions:
Despite the challenges, several solutions can help mitigate the environmental impact of technology hardware:
- Design for sustainability: Manufacturers should design hardware with longer lifespans, repairability, and energy efficiency.
- Resource efficiency: Utilizing recycled materials and exploring alternative resources can minimize resource depletion.
- Renewable energy: Shifting to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power for hardware production and data centers can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Circular economy: Implementing a circular economy model where e-waste is recycled and reused can minimize waste and promote resource recovery.
- Consumer awareness: Educating consumers about the environmental impact of their hardware choices can encourage responsible consumption and longer device lifespans.
By adopting these solutions and promoting sustainable practices throughout the entire lifecycle of technology hardware, we can minimize its environmental impact and build a greener future.
